Please wait...
From basic terminologies to understanding the core concepts & techniques, our guide & definitions will help parents who are looking for the right Abacus program for their children.
Get started now and take your abacus knowledge to the next level!
An abacus is an ancient counting tool that has been used for thousands of years to perform arithmetic calculations. Often made of a rectangular frame with rods or wires, each containing beads that can be moved back and forth, the abacus serves as both a visual and tactile aid for performing addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Its origins trace back to ancient Mesopotamia, and it has since evolved into various forms across dierent cultures, from the Chinese suanpan to the Japanese soroban. Although modern calculators and computers have largely replaced the abacus, it remains an important educational tool and a symbol of the human ingenuity in developing practical devices for mathematics.

An instrument/tool that consists of a frame with rods or wires, each holding beads that represent numbers. It is used for performing arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division by manipulating beads along rods.
The wooden structure that holds the rods and beads together.
The movable objects on the abacus that represent digits. The beads are moved up and down the rods to perform calculations.
The value of each column of beads, with the rightmost column representing one's place.

Similar to the Chinese Abacus, but with fewer beads. It typically has 13 rods, each with one bead on the upper deck and four beads on the lower deck.
The wires or vertical columns on the abacus that the beads slide on.
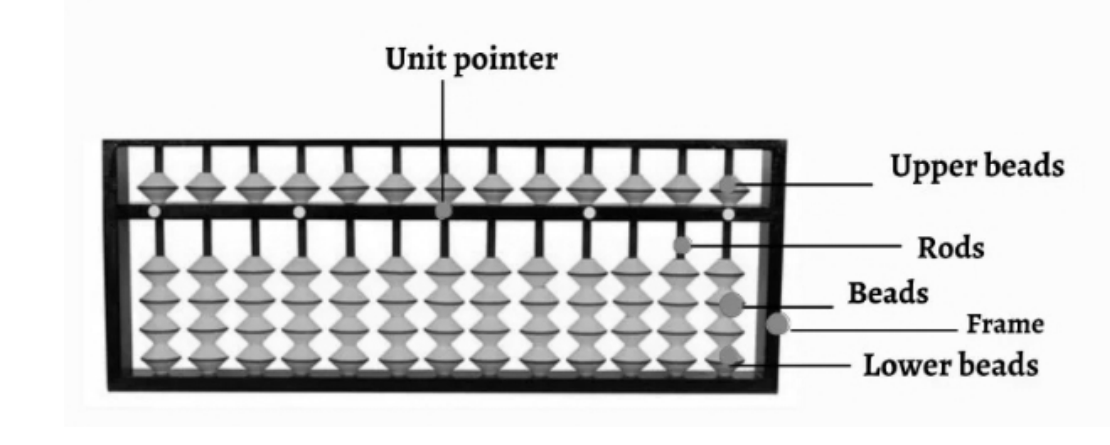
The two sections of the abacus separated by a horizontal beam.
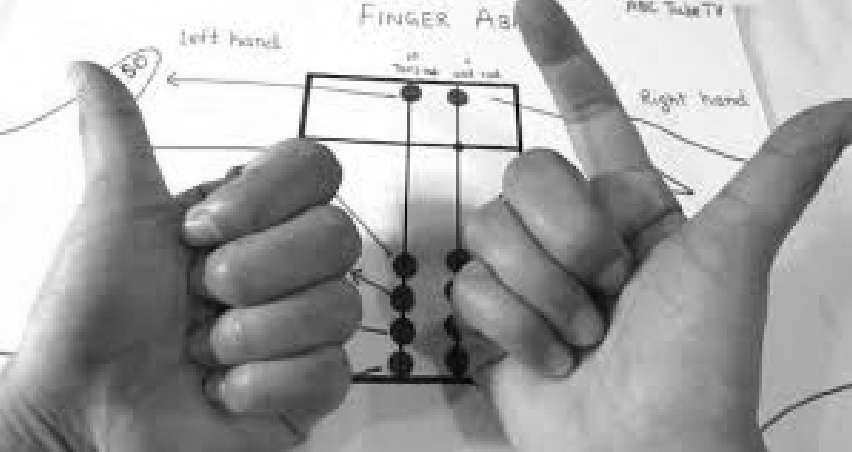
A mental math technique used by UCMAS wherein children use three fingers from each hand to move beads on the abacus to solve math problems. The technique is designed to stimulate the brain regions associated with numbers, memory, and problem-solving.
Mental math refers to the process of performing arithmetic calculations in your head, without the use of a calculator, pen, paper, or other external aids. It involves quickly and eciently solving problems using your cognitive abilities, such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and more complex operations, all done mentally. Mental math is an important skill that helps improve number sense, problem-solving abilities, and cognitive agility. It is often practiced to enhance numerical fluency, speed, and accuracy in everyday situations.
Also called mental arithmetic, it refers to one’s ability to perform math calculations in their head without using a calculator, pencil, or paper.
Vedic mathematics is a system of mental calculation techniques that originated in ancient India. It uses a set of 16 sutras (formulae) and 13 sub-sutras (subformulae) to solve mathematical problems quickly and eciently.
Abacus math is a method of performing arithmetic calculations using an abacus. It involves manipulating beads on the abacus for performing mathematical operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
A learning style where children learn using images, colors, graphics etc. Forming and recalling images of numbers through abacus beads activates this style.
A learning style refers to the preferred way in which an individual processes, understands, and retains information. It is the unique approach a person uses to take in, process, and comprehend new material, and it can be influenced by various factors such as cognitive processes, sensory preferences, and personal experiences. While theories about learning styles can dier, they often categorize individuals into groups based on dominant modes of learning, such as visual, auditory, or kinesthetic, and sometimes even social or solitary learning preferences.
Also known as kinesthetic learning, it is a learning style that involves learning through physical interaction and touch. UCMAS uses the physical abacus for tactile learning, through which students learn by using their sense of touch.
A learning style where someone learns by listening to the information. UCMAS programs employ auditory learning where children perform arithmetic calculations by listening to numbers at extremely high speeds.
A learning style where children learn using images, colors, graphics etc. Forming and recalling images of numbers through abacus beads activates this style.
Cognitive skills, also known as thinking skills or intellectual abilities, are the mental processes that allow us to acquire, process, store, and use information. Some such skills are visual-spatial skills, attention and concentration, memory and recall, problem-solving skills, critical thinking skills, creativity and imagination.
Visual skills are the ability to interpret and make sense of what the eyes see. They are important for many everyday activities, such as reading, writing, eating, and dressing.
It includes one’s ability to pay attention and effectively interpret what other people are saying. UCMAS programs include listening exercises as part of its curriculum.
Auditory skills are the ability to process what one hears. It includes one’s ability to detect, discriminate, recognize and remember different sounds.
Fine motor skills are the precise movements of the small muscles in the hands, fingers, feet, and toes. Using the 6 finger technique to manipulate an abacus helps develop a child’s fine motor skills and hand-eye coordination.

It is a breakdown of the cognitive skills that your child will develop through the scientifically designed program at UCMAS:
Concentration
Observation
Memory
Imagination
Creativity
Judgment
Application
Reasoning
Self-confidence
Holistic development is the growth of a person's social, emotional, physical, mental, and intellectual aspects. It's about a child's overall well-being, not just their academic progress.
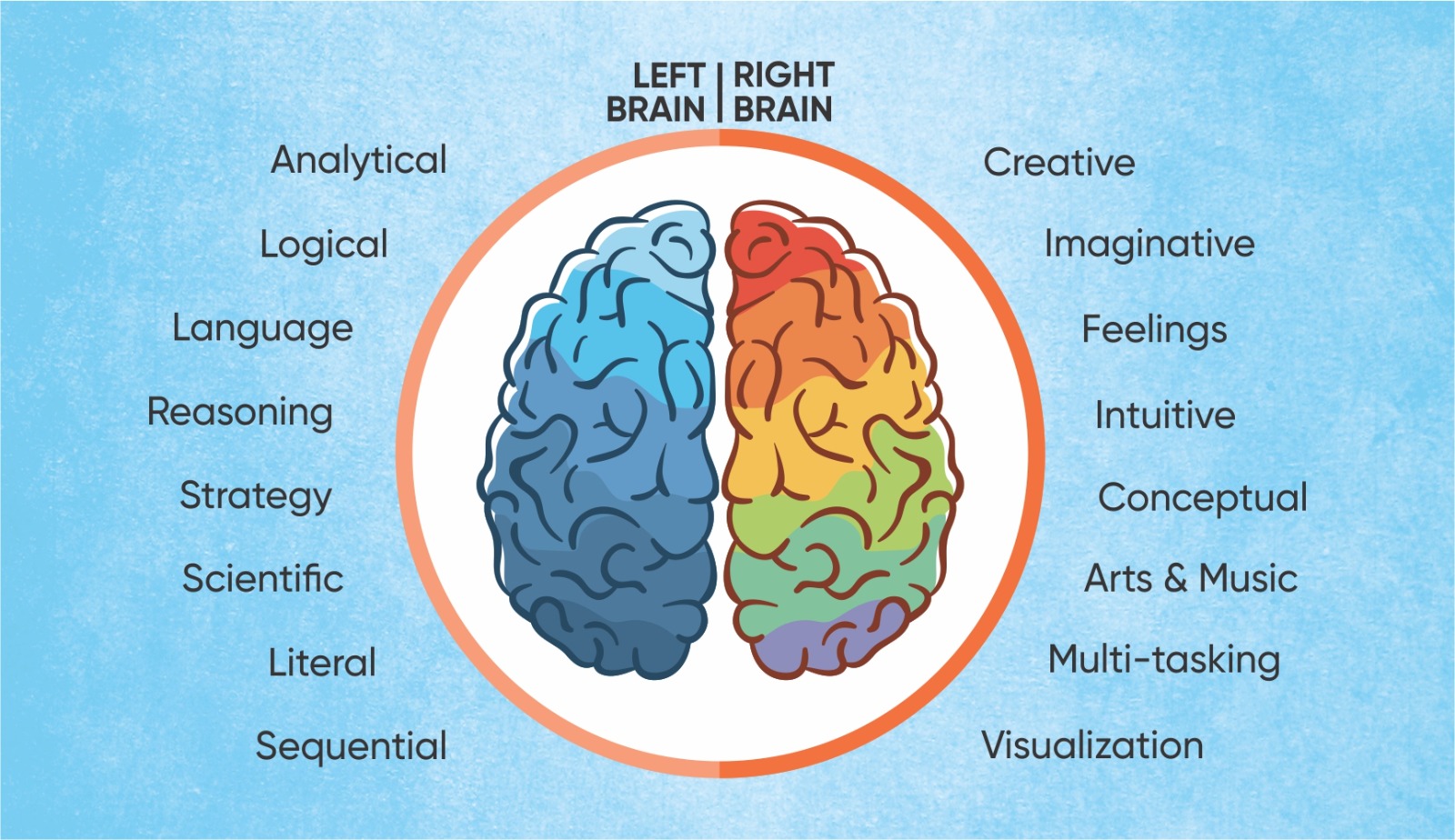
Whole brain development refers to the idea of stimulating both the left and right hemispheres of the brain. This approach aims to enhance cognitive abilities, creativity, and overall intellectual potential.
The left hemisphere of the brain is often associated with logical, analytical thinking, language skills, and sequential processing. It's considered the "academic" side, responsible for functions like math, science, and reading.
The right hemisphere of the brain is often associated with creativity, intuition, and spatial awareness. It's considered the "artistic" side, responsible for functions like music, art, and imagination.
A teaching method used by UCMAS to help children develop mental math skills and their visual learning style. Children look at numbers on flashcards and perform calculations.
UCMAS mental math worksheets are designed for children aged 5-13, including exercises in basic arithmetic, mental calculation drills, word problems, pattern recognition, and number sense. Solving these worksheets can help enhance children’s speed, accuracy, and problem-solving abilities.
These are digital or physical games that make learning math fun and engaging. They often involve puzzles, challenges, and real-world scenarios, making the learning process enjoyable and interactive.
It is a multi-sensory learning approach at UCMAS that combines visual, auditory, and tactile learning. Children learn by seeing numbers on the abacus, hearing instructions, and physically manipulating the beads. This holistic approach enhances understanding, memory retention, and problem-solving skills.
These are digital platforms by UCMAS that provide additional learning materials and practice exercises. They can include videos, tutorials, quizzes, and interactive simulations, offering flexibility and personalized learning experiences.